MIXING PROCESSES
MAP mixers are highly versatile and suitable for a wide range of processes in solids mixing technology. They effectively mix dry powdery materials, incorporate small amounts of liquids, and facilitate the agglomeration or granulation of powders with the addition of liquids. Additionally, MAP mixers are used for drying moist media and coating materials. They are also used for thorough homogenisation in resting chambers as well as for crumbling lumpy substances. Their adaptability makes them ideal for various applications across industries where precision, consistency, and efficiency in processing solids and powders are essential.
Powder mixing
MAP mixers are engineered for efficiently mixing a variety of solids. Depending on the task, up to 20 different individual components may need to be mixed together. The design of the MAP mixer ensures that the entire product chamber is involved in the mixing process, facilitating cavity-free homogenisation. Depending on the configuration of the mixing tools or the speed of the mixer, agitation can range from gentle to high turbulence. For solid mixtures or solid-liquid combinations, the achieved mixing quality can reach ±1% in relation to the added components, depending on the specific characteristics of the products.
Powder Mixing with liquid addition
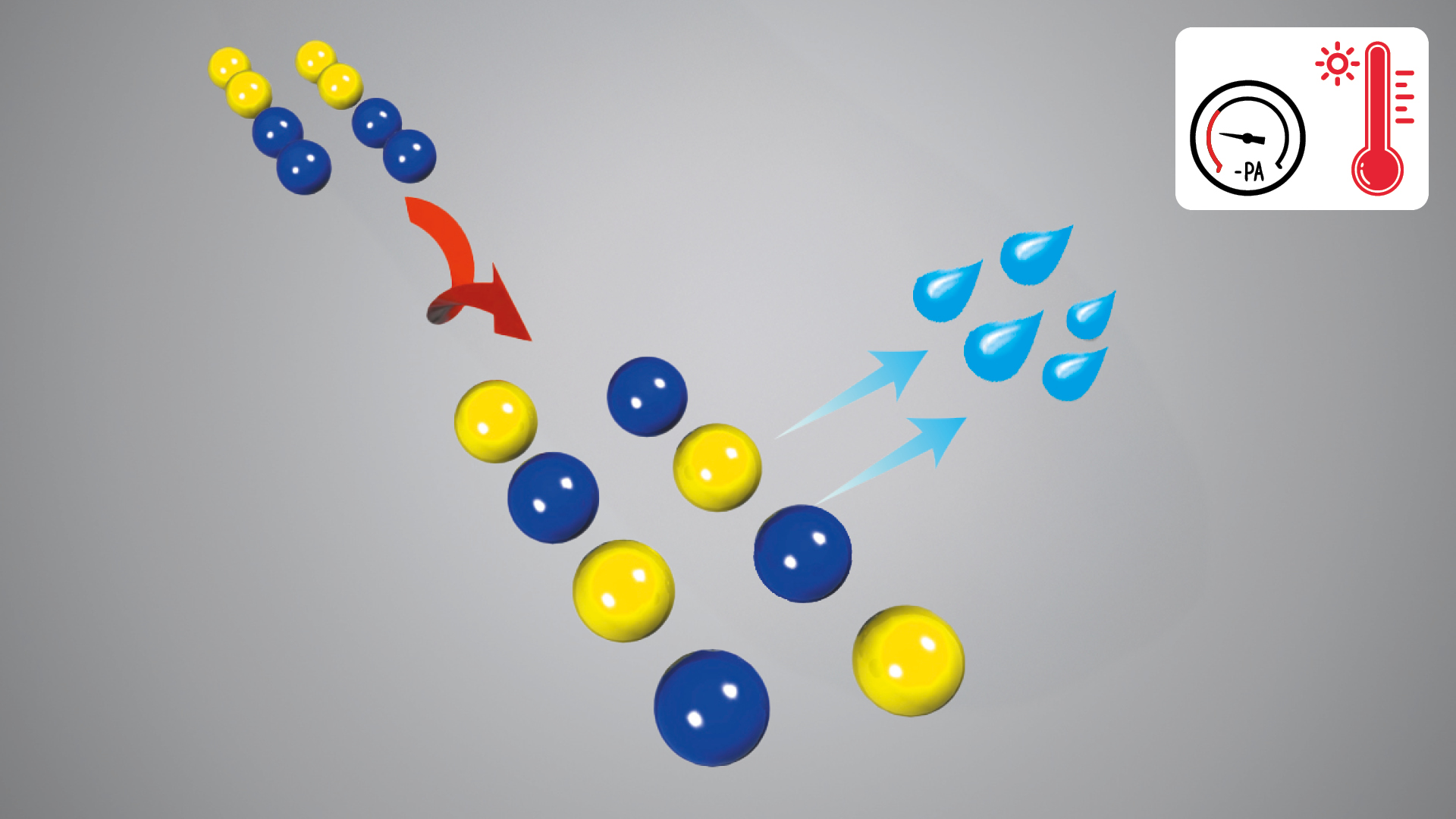
Numerous applications focus on converting powdery, dusty bulk materials into a dust-free form through the addition of small amounts of liquids. In the MAP mixer, these bulk materials are thoroughly mixed with the liquid component, resulting in a dust-free bulk material that can be efficiently fed into open loading and transport systems. MAP’s batch and continuous mixers are particularly well-suited for this application, providing very short retention time on compact machines. Existing installations have achieved throughputs exceeding 1,000 m³/h, demonstrating the efficiency and effectiveness of MAP mixing technology in handling large volumes of material.
Agglomerating / Granulating
In MAP mixing machines, the powdery solid component is brought into intensive contact with a suitable liquid binding agent. This process facilitates the interconnection of solid particles through agglomeration, resulting in the formation of spherical or crumb-like granules. By carefully controlling the mixing intensity and the generated shear forces, various sizes of agglomerates can be produced. The stability of the resulting granules can range from low to medium, depending on the strength of the binding agent used. If further drying of the granules is necessary, it should be conducted gently through convective drying methods to preserve the integrity of the product.
Drying
coating
Resting & Homogenising
Crumbling
Heating / Cooling
Froude number and physical effect
The horizontal MAP single-shaft mixer, utilising ploughshare-type mixing tools and the fluidised bed principle, epitomises efficient industrial mixing technology. Within fractions of a second, it achieves significant intermixing of dry components. Key to its operation is the Froude number, determining forces within the mixing process. With adaptable configurations, it balances mixing time and quality across various industrial applications, showcasing MAP's innovation and excellence.
Click the video on the right showing the computer simulation of mixing two components in a WBH batch mixer with ploughshare tools.